

.png)
Pharmacy Technician
As you know that Pharmacy Technician is one one on the most valuable Diploma in medical profession and as the calculation every year almost 50,000 students appear in Pharmacy technician Exams.
Every student is finding some helping meterial for their studies. Today we give you all types of documents that you need so stay with us and for information please join our Whatsapp Group by clicking on the link here Medicosia Whatsapp Group.
Pharmacy Technician Practical List (1st Year)
Pharmacy Technician Practical List (2nd Year)
Pharmacy Technician Paper Sample
Sample Paper for 1st Year (Part 1) Download
Sample Paper for 1st Year (Part 2) Download
Sample Paper for 2nd Year (Part 1) Download
Sample Paper for 2nd Year (Part 2) Download

6 Common health issues in Pakistan
6 Common health issues in Pakistan
- HIV/AIDS
- Polio
- Dengue Fever
- Hepatitis
- Malaria
- Respiratory Tract Infection
How You Can Prevent from Diseases
- Eat Healthy. Eating healthy helps prevent, delay, and manage heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other chronic diseases.
- Get Regular Physical Activity.
- Avoid Drinking Too Much Alcohol.
- Get Screened.
- Take Care of Your Teeth.
- Get Enough Sleep.

Muscle spasms in lower back
Muscle spasms in lower back
 |
| Muscle spasms in lower back |
What is Muscle spasms in lower back:
Muscle fits in the lower back can be an excruciating and crippling experience for some people. These compulsory compressions of the muscles can strike abruptly and upset day to day exercises. In this article, we will dive into the causes, side effects, anticipation, and treatment choices for muscle fits in the lower back while keeping site design improvement as a top priority to guarantee you find the data you want.
Reasons for Muscle Fits in the Lower Back
Muscle fits in the lower back can happen because of multiple factors. Understanding the basic causes is significant for successful avoidance and the board. A few normal elements adding to these fits include:
Muscle Abuse:
Overexertion of the lower back muscles, frequently because of truly difficult work or inordinate activity, can prompt fits.
Drying out:
Lacking liquid admission can cause electrolyte uneven characters, which might set off muscle fits.
Unfortunate Stance:
Sitting or remaining with ill-advised stance can strain the lower back muscles over the long run, bringing about fits.
Muscle Lopsided characteristics:
Powerless or tight muscles in the lower back and mid-region can build the gamble of fits.
Injury:
Injury or injury to the lower back, for example, a herniated plate or sprain, can prompt muscle fits as a defensive reaction.
Symptoms of Lower Back Muscle Spasms
Identifying the symptoms of lower back muscle spasms is crucial for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
 |
| Symptons of low Back Pain |
- Sudden, sharp pain in the lower back
- Muscle stiffness and tightness
- Limited range of motion
- Muscle twitching or jerking
- Pain that radiates down the legs (if nerve compression is involved)
Preventing Muscle Spasms in the Lower Back
Avoidance is much of the time the best way to deal with overseeing lower back muscle fits. Here are a few hints to decrease the gamble:
Keep up with Great Stance:
Be aware of your stance while sitting, standing, and lifting weighty items.
Remain Hydrated:
Drink a lot of water to guarantee your muscles have satisfactory hydration and electrolytes.
Stretch and Reinforce:
Ordinary extending and fortifying activities for the lower back and center muscles can assist with forestalling fits.
Utilize Appropriate Lifting Procedures:
While lifting objects, twist your knees and keep the article near your body to limit burden on the lower back.
Warm-Up Before Exercise:
In every case warm up prior to participating in difficult actual work to set up your muscles.
 |
| Treatment for lower back pain |
Treating Lower Back Muscle Fits
On the off chance that you truly do encounter a muscle fit in your lower back, here are a moves toward ease the aggravation and distress:
Rest:
Give your muscles time to recuperate by keeping away from arduous exercises.
Apply Intensity or Ice:
Applying intensity or ice to the impacted region can assist with diminishing agony and irritation.
Delicate Extending:
Delicate extending activities can loosen up the muscles and give alleviation.
Over-the-Counter Agony Drugs:
Non-remedy pain killers like ibuprofen can be useful for transient help.
Counsel a Medical care Proficient:
In the event that the fits continue or are joined by extreme torment, counsel a medical services supplier for a legitimate assessment and therapy plan.

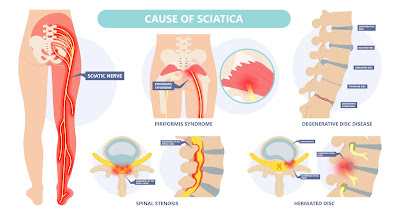
Sciatica Pain (درد شیٹیکا)
Sciatica Pain (درد شیٹیکا)
 |
| Sciatica Pain |
درد ا شیاٹیکا کیا ہے ؟
sciatic nerve جسم کا سب سے بڑا اعصاب ہے اور sciatica اعصابی درد ہے جو sciatic اعصاب کی جلن کی وجہ سے ہوتا ہے۔ وہ درد جو ٹانگ کے خراب درد کی طرح محسوس ہو سکتا ہے، یا شوٹنگ کا درد ہو سکتا ہے جو کھڑے ہونا یا بیٹھنا تقریباً ناممکن بنا دیتا ہے، عام طور پر کمر کے نچلے حصے سے لے کر ران کے پیچھے تک محسوس ہوتا ہے اور گھٹنے کے نیچے تک پھیلتا ہے۔ اگر آپ کو سائیٹیکا ہے تو آپ کو کمزوری، بے حسی، یا آپ کی ٹانگ کے نیچے، یا یہاں تک کہ آپ کی انگلیوں میں جلن یا جھنجھناہٹ کا احساس ہوسکتا ہے۔ آپ اپنے گھٹنے کو موڑنے یا پاؤں اور انگلیوں کو حرکت دینے میں بھی ناکامی کا تجربہ کر سکتے ہیں۔ Sciatica اچانک ہو سکتا ہے یا یہ آہستہ آہستہ ترقی کر سکتا ہے.
sciatica کی وجوہات کیا ہیں؟
Sciatica عام طور پر 'پنچڈ اعصاب' کی علامت ہوتی ہے جو ریڑھ کی ہڈی کے نچلے حصے میں سے ایک یا زیادہ کو متاثر کرتی ہے۔ ٹانگ سے گزرتے ہوئے اعصاب ریڑھ کی ہڈی کے اندر یا باہر چٹکی بجا سکتا ہے۔
sciatica کی کچھ وجوہات میں شامل ہیں:
- ایک ہرنیٹڈ یا سلپڈ ڈسک: جو sciatica کی سب سے عام وجہ ہے جو اعصابی جڑ پر دباؤ کا سبب بنتی ہے۔
- Piriformis syndrome: جو اس وقت ہوتا ہے جب چھوٹے piriformis عضلات، جو کولہوں میں گہرے ہوتے ہیں، تنگ اور اینٹھن ہو جاتے ہیں، اس طرح sciatic اعصاب پر دباؤ پڑتا ہے اور اس میں جلن ہوتی ہے۔
- اسپائنل سٹیناسس: اس کا نتیجہ ریڑھ کی نالی کے تنگ ہونے سے ہوتا ہے جو اعصاب پر دباؤ ڈالتا ہے۔
- Spondylolisthesis: یہ اس وقت ہوتا ہے جب ایک فقرہ پھسل جاتا ہے، تاکہ یہ اس کے اوپر والے سے باہر ہو، اس سوراخ کو تنگ کرتا ہے جس سے اسکائیٹک اعصاب نکلتا ہے۔
sciatica کے خطرے کے عوامل کیا ہیں؟
sciatica کے خطرے کے عوامل میں شامل ہیں:
بڑھتی عمر کی وجہ سے ریڑھ کی ہڈی میں تبدیلیاں، جیسے ہرنیٹڈ ڈسک اور ہڈیوں کے اسپرس
موٹاپا ہونا جو ریڑھ کی ہڈی پر دباؤ ڈالتا ہے۔
طویل عرصے تک بیٹھنا
ایک بیہودہ طرز زندگی کی قیادت
ذیابیطس
ایسی ملازمتیں جن کے لیے آپ کو بھاری بوجھ اٹھانے، طویل عرصے تک گاڑی چلانے، بار بار اپنی پیٹھ مروڑنے کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے۔
sciatica کی علامات کیا ہیں؟ اسکیاٹیکا کی تشخیص کیسے کی جاتی ہے؟
sciatica کی عام علامات میں شامل ہیں:
کمر کے نچلے حصے کا درد
پیچھے یا ٹانگ میں درد جو بیٹھتے وقت بدتر ہوتا ہے۔
کولہے کا درد
ٹانگ میں جلن یا جھنجھلاہٹ
کمزوری، بے حسی، یا ٹانگ یا پاؤں کو حرکت دینے میں دشواری
پیچھے کے ایک طرف مستقل درد
شوٹنگ کا درد جو کھڑا ہونا مشکل بناتا ہے۔
تشخیص
اگر آپ sciatica کی علامات میں مبتلا ہیں تو آپ کو ایک جنرل فزیشن سے ملنے کی ضرورت ہے۔ جنرل فزیشن، بدلے میں، آپ کی حالت کی بنیاد پر آپ کو کسی آسٹیو پیتھک ڈاکٹر یا ایک کائروپریکٹر کے پاس بھیج سکتا ہے۔
ڈاکٹر آپ سے آپ کی طبی تاریخ، آپ کے پیشے، آپ کی روزمرہ کی سرگرمیوں اور آپ کے درد سے متعلق سوالات جیسے کہ:
آپ کو درد کہاں محسوس ہوتا ہے؟
کیا یہ آپ کی ٹانگ کے نیچے ہے؟ کیا یہ دونوں ٹانگوں میں ہے؟ کیا یہ آپ کے گھٹنے پر رک جاتا ہے؟
اپنے درد کو 1-10 کے پیمانے پر درجہ بندی کریں اور 10 بدترین ہونے کے ساتھ۔
کیا آپ کو اپنی ٹانگوں اور/یا پیروں میں کمزوری یا جھنجھلاہٹ کا سامنا ہے؟
آپ نے حال ہی میں کون سی سرگرمیاں کیں؟
کیا درد کو کم کرتا ہے یا اسے بدتر بناتا ہے؟
آپ کا ڈاکٹر جسمانی بھی کرے گا اور آپ کو اعصابی امتحان سے گزرنے کا مشورہ دے گا۔ جسمانی امتحان میں، ڈاکٹر آپ کی کرنسی، حرکت کی حد، اور آپ کی ریڑھ کی ہڈی کی جانچ کرے گا۔
اعصابی امتحان کے دوران، ڈاکٹر آپ کے اضطراب، پٹھوں کی طاقت، اور دیگر اعصابی تبدیلیوں کی جانچ کرے گا۔ وہ آپ کو امیجنگ ٹیسٹ، ایکسرے، کیٹ اسکین اور ایم آر آئی ٹیسٹ لینے کا مزید مشورہ دے سکتا ہے۔
یہ تمام ٹیسٹ آپ کے ڈاکٹر کو مکمل تصویر فراہم کریں گے۔
sciatica کی پیچیدگیاں کیا ہیں؟
اسکیاٹیکا کی وجہ سے پیچیدگیاں نایاب ہیں۔ اگر وہ واقع ہوتے ہیں تو ان میں شامل ہو سکتے ہیں:
مستقل اعصابی نقصان
متاثرہ ٹانگ میں احساس کا نقصان
متاثرہ ٹانگ میں کمزوری
آنتوں یا مثانے کے کام کا نقصان
sciatica کا علاج کیا ہے؟
Sciatica کے لئے طبی علاج
sciatica کے لیے اکثر جسمانی تھراپی تجویز کی جاتی ہے۔ آپ کا ڈاکٹر تجویز کر سکتا ہے کہ آپ کمر کی کچھ مشقیں اور اسٹریچ کریں۔ اگر کوئی بہتری نہیں آتی ہے تو آپ ڈاکٹر سے متبادل علاج کے بارے میں پوچھ سکتے ہیں کیونکہ بہت سے لوگوں کو فزیکل تھراپسٹ، آسٹیو پیتھس اور کائروپریکٹر کے پاس جانے سے راحت ملتی ہے۔
مستقل سائیٹیکا کے معاملات میں، ڈاکٹر ایپیڈورل انجیکشن تجویز کر سکتا ہے جو سٹیرایڈ انجیکشن ہیں۔
سنگین صورتوں میں، ڈاکٹر سرجری کی سفارش کر سکتا ہے۔
ورزش
Sciatica مشقیں عام طور پر ریڑھ کی ہڈی کے کالم اور پٹھوں اور کنڈرا کو مضبوط بنانے اور کھینچنے پر مرکوز ہوتی ہیں۔ یوگا اور پیلیٹس تیراکی اور چہل قدمی کے ساتھ ورزش کی اچھی شکلیں ہیں۔ ورزش کے طریقہ کار کا فیصلہ کرنے سے پہلے یہ معلوم کرنے کے لیے اپنے ڈاکٹر سے مشورہ کریں کہ ورزش کی کونسی شکل آپ کے لیے بہترین ہے۔ یہ بھی مشورہ دیا جاتا ہے کہ مشقیں نگرانی میں کریں، جب تک کہ آپ اعتماد محسوس نہ کریں۔

Top 20 Hospitals in Multan
 |
Top 20 Hospitals in Multan |
Top 20 Hospitals in Multan
| SR NO. | HOSPITALS NAME | ADDRESS | PHONE NUMBER |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ibne Sina Hospital | Northern Bypass, Block A Model Town, Multan, Punjab | 061-6782873 |
| 2 | Aziz Hospital | Aziz Hotel Chowk، Nawab Khan St, Multan | 061-4543786 |
| 3 | Mukhtar A Sheikh Memorial Welfare Hospital | Khanewal Road, Near Pak Arab Fertilizers, Shah Rukn E Alam Town, Multan, Punjab 60000 | 061-4554800 |
| 4 | Mission Hospital Multan | 85 Nusrat Road, Near SP Chawk, Multan Cantonment, Multan, Punjab 60000 | 061-4540052 |
| 5 | Waheeda Khanum Hospital | 6F7Q+R9H, Al Mustafa Colony, Shamsabad Colony, Multan, Punjab | 061-4782228 |
| 6 | Chenab General Hospital | Chungi No 1, Suraj Miani Road, Near Jamilabad Colony, Multan, Punjab | 061-4518874 |
| 7 | Combined Military Hospital Multan | Ghaus Ul Azam Road, Near Naseem Hayat Road, Pia Colony, Multan, Punjab 60000 | 061-9201703 |
| 8 | Jinnah Hospital | Nishtar Road, Al Rahim Colony, Multan, Punjab 60000 | 061-4781470 |
| 9 | Medicare Hospital | 62 A Abdali Road, Altaf Town, Multan, Punjab 60000 | 061-4581702 |
| 10 | Punjab Hospital | New Multan Service Road, X Block, New Multan Colony, Multan, Punjab | 061-4556810 |
| 11 | City Hospital | La Salle Road, Peer Khurshid Colony Chah Usman Wala, Multan, Punjab | 061-6510367 |
| 12 | Bakhtawar Amin Memorial Hospital Multan | Multan Bypass, Multan, Punjab | 0304-8792904 |
| 13 | Zubaida Fatima Memorial Hospital | 5FCQ+VC3, Gulzaib Colony, Multan, Punjab 60600 | 0300-6345255 |
| 14 | Gulgasht Hospital | Bosan Road, North Gulgasht Colony, Multan, Punjab | 061-6513068 |
| 15 | Hamida sharif Hospital | Block V New Multan Colony, Multan, Punjab | 0300-8633766 |
| 16 | Haleema Hospital Complex | 4 Nishtar Road, Al Rahim Colony, Multan, Punjab 60000 | 0302-8637774 |
| 17 | Multan Medical Mission Hospital | 6F5M+8W6, Wahdat Colony Multan, Punjab | 061-4424757 |
| 18 | Care Family Hospital | Main Road, Gulshan-E-Iqbal Qasim Bela, Multan, Punjab | 061-6350751 |
| 19 | Maryum Medical Center | 6G46+R38, Block S New Multan Colony, Multan, Punjab | 061-6561043 |

Caring for Your Eyes: Understanding and Treating Eye Flu
 |
| Eye Flu |
تعارف
آئی فلو، علاج کے طور پر آشوب چشم کے نام سے جانا جاتا ہے، آنکھوں کی ایک عام حالت ہے جو پوری دنیا میں لوگوں کی ایک بڑی تعداد کو متاثر کرتی ہے۔ اگرچہ یہ عجیب اور حیرت انگیز طور پر پریشان کن ہوتا ہے، خوش قسمتی سے یہ عام طور پر کوئی مشکل حالت نہیں ہے اور اس کا مؤثر طریقے سے علاج کیا جا سکتا ہے۔ اس آرٹیکل میں، ہم آنکھوں کے انفلوئنزا کی وجوہات، ضمنی اثرات اور طاقتور ادویات کی تحقیق کریں گے، اس کے علاوہ ویب سائٹ کے ڈیزائن کو بڑھانے کے لیے کچھ تجاویز کے بارے میں بھی بات کریں گے تاکہ آپ کو بہتر طور پر سمجھنے اور اس حالت سے نمٹنے میں مدد ملے۔آنکھ کا فلو (آشوب چشم) کیا ہے؟
آشوب چشم، جسے اکثر "آئی انفلوئنزا" یا "گلابی آنکھ" کہا جاتا ہے، آشوب چشم کا بڑھ جانا ہے، پتلی اور سیدھی فلم جو آنکھ کے سفید ٹکڑے (اسکلیرا) اور پلکوں کی اندرونی سطح کو ڈھانپتی ہے۔ اس اضطراب کو مختلف عناصر کے ذریعے لایا جا سکتا ہے، بشمول وائرل یا بیکٹیریل بیماریاں، حساسیت، یا دھواں یا باقیات جیسی بڑھوتری۔آنکھوں کے فلو کی وجوہات
وائرل بیماریاں:
انفیکشنز، مثال کے طور پر، اڈینو وائرس وائرل آشوب چشم کی ایک عام وجہ ہیں۔ یہ بہت زیادہ متعدی ہے اور کسی داغدار فرد کی آنکھوں کے اخراج کے ساتھ فوری یا گردشی رابطے سے پھیل سکتا ہے۔بیکٹیریل آلودگی:
بیکٹیریل آشوب چشم اکثر Staphylococcus یا Streptococcus جرثوموں کے ذریعے لایا جاتا ہے۔ یہ اسی طرح غیر معمولی طور پر متعدی بھی ہو سکتا ہے اور بدقسمتی سے ہاتھ کی صفائی یا آلودہ سطحوں سے رابطے کا نتیجہ ہو سکتا ہے۔انتہائی حساس ردعمل:
نامناسب طور پر حساس آشوب چشم اس وقت ہوتا ہے جب آشوب چشم الرجین جیسے دھول، پالتو جانوروں کی خشکی، یا باقی پرجیویوں کو جواب دیتا ہے۔ یہ متعدی نہیں ہے اور عام طور پر دونوں آنکھوں کو متاثر کرتا ہے۔اضطراب:
دھواں، آلودگی، یا مصنوعی مرکبات جیسی اشتعال انگیزیوں کے لیے کشادگی آشوب چشم کو بڑھا سکتی ہے۔ اس قسم کا آنکھ کا انفلوئنزا متعدی نہیں ہے اور عام طور پر اس وقت ٹھیک ہو جاتا ہے جب اس کی شدت ختم ہو جاتی ہے۔آنکھ کے فلو کی علامات
آنکھوں کے فلو کی عام علامات میں شامل ہو سکتے ہیں:- ایک یا دونوں آنکھوں میں لالی۔
- آنکھوں سے پانی یا پیپ کی طرح خارج ہونا۔
- خارش یا جلن کا احساس۔
- آنکھوں میں سختی کا احساس۔
- روشنی کی حساسیت میں اضافہ۔
- سوجی ہوئی پلکیں۔
- دھندلا ہوا نقطہ نظر (کم عام)۔
آنکھ کے فلو کا موثر علاج
آنکھ کے فلو کا علاج اس کی بنیادی وجہ پر منحصر ہے:وائرل آشوب چشم:
چونکہ وائرل آشوب چشم ایک وائرس کی وجہ سے ہوتا ہے، اس لیے یہ اینٹی بایوٹک کا جواب نہیں دیتا۔ علاج میں عام طور پر گرم کمپریسس اور مصنوعی آنسو سے علامات کو دور کرنا شامل ہوتا ہے۔ آرام اور اچھی حفظان صحت بشمول بار بار ہاتھ دھونے سے وائرس کے پھیلاؤ کو روکنے میں مدد مل سکتی ہے۔بیکٹیریل آشوب چشم:
بیکٹیریل آشوب چشم کا علاج عام طور پر اینٹی بائیوٹک آئی ڈراپس یا مرہم سے کیا جاتا ہے۔ تکرار کو روکنے کے لیے اینٹی بائیوٹکس کا پورا کورس مکمل کرنا ضروری ہے۔الرجک آشوب چشم:
الرجین سے بچنا اور اینٹی ہسٹامائن آئی ڈراپس کا استعمال الرجک آشوب چشم کی علامات کو کم کرنے میں مدد کر سکتا ہے۔ الرجسٹ سے مشورہ طویل مدتی انتظام کے لیے فائدہ مند ہو سکتا ہے۔آشوب چشم:
جلن کو دور کرنے اور مصنوعی آنسو استعمال کرنے سے علامات کو دور کرنے میں مدد مل سکتی ہے۔ ممکنہ خارش والے ماحول میں حفاظتی چشمہ پہننا تکرار کو روک سکتا ہے۔آنکھوں کے فلو کے پھیلاؤ کو روکنا
آنکھوں کے فلو کے پھیلاؤ کو روکنے کے لیے، ان تجاویز پر عمل کریں:
- اپنے ہاتھ بار بار دھوئیں، خاص طور پر اپنی آنکھوں کو چھونے کے بعد۔
- اپنی آنکھوں کو چھونے یا رگڑنے سے گریز کریں۔
- تولیے، تکیے، یا آنکھوں کا میک اپ دوسروں کے ساتھ نہ بانٹیں۔
- اگر آپ کو آنکھ کا فلو ہے تو، علامات کے حل ہونے تک دوسروں کے ساتھ قریبی رابطے سے گریز کریں۔
- ان سطحوں کو جراثیم سے پاک کریں جو آنکھوں کے رطوبتوں کے ساتھ رابطے میں آسکتی ہیں۔
یاد رکھیں، اگر آپ کو شبہ ہے کہ آپ کو آنکھ کا فلو ہے یا آپ کو مستقل علامات کا سامنا ہے، تو مناسب تشخیص اور مناسب علاج کے منصوبے کے لیے آنکھوں کی دیکھ بھال کرنے والے پیشہ ور سے مشورہ کریں۔
Introduction
Eye flu, therapeutically known as conjunctivitis, is a typical eye condition that influences a huge number of individuals around the world. While it tends to be awkward and, surprisingly, excruciating, fortunately it is normally not a difficult condition and can be effectively treated. In this article, we will investigate the causes, side effects, and powerful medicines for eye influenza, while additionally talking about some Website design enhancement advancement tips to assist you with better comprehension and deal with this condition.
What Is Eye Flu (Conjunctivitis)?
Conjunctivitis, frequently alluded to as "eye influenza" or "pink eye," is the aggravation of the conjunctiva, the slim and straightforward film covering the white piece of the eye (sclera) and the internal surface of the eyelids. This aggravation can be brought about by different elements, including viral or bacterial diseases, sensitivities, or aggravations like smoke or residue.
Causes of Eye Flu
- Viral Diseases:
Infections, for example, adenoviruses are a typical reason for viral conjunctivitis. It is profoundly infectious and can spread through immediate or circuitous contact with a tainted individual's eye emissions.
- Bacterial Contaminations:
Bacterial conjunctivitis is frequently brought about by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus microbes. It can likewise be exceptionally infectious and may result from unfortunate hand cleanliness or contact with polluted surfaces.
- Hypersensitive Responses:
Unfavorably susceptible conjunctivitis happens when the conjunctiva responds to allergens like dust, pet dander, or residue parasites. It isn't infectious and typically influences the two eyes.
- Aggravations:
Openness to aggravations like smoke, contamination, or synthetic compounds can prompt aggravation conjunctivitis. This sort of eye influenza isn't infectious and commonly settle when the aggravation is eliminated.
Symptoms of Eye Flu
Common symptoms of eye flu may include:
- Redness in one or both eyes.
- Watery or pus-like discharge from the eyes.
- Itchy or burning sensation.
- Gritty feeling in the eyes.
- Increased sensitivity to light.
- Swollen eyelids.
- Blurred vision (less common).
Effective Treatment for Eye Flu
The treatment of eye flu depends on its underlying cause:
- Viral Conjunctivitis:
Since viral conjunctivitis is caused by a virus, it does not respond to antibiotics. Treatment typically involves relieving symptoms with warm compresses and artificial tears. Rest and good hygiene, including frequent handwashing, can help prevent the spread of the virus.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis:
Bacterial conjunctivitis is usually treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointments. It's essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics to prevent recurrence.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis:
Avoiding allergens and using antihistamine eye drops can help alleviate symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis. Consultation with an allergist may be beneficial for long-term management.
- Irritant Conjunctivitis:
Removing the irritant and using artificial tears can help relieve symptoms. Wearing protective eyewear in environments with potential irritants can prevent recurrence.
Preventing the Spread of Eye Flu
To prevent the spread of eye flu, follow these tips:
- Wash your hands frequently, especially after touching your eyes.
- Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes.
- Do not share towels, pillows, or eye makeup with others.
- If you have eye flu, avoid close contact with others until symptoms resolve.
- Disinfect surfaces that may come into contact with eye secretions.
Eye flu, or conjunctivitis, is a common eye condition with various causes, including viral and bacterial infections, allergies, and irritants. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment is essential for a quick recovery and to prevent its spread. . By following good hygiene practices and seeking medical advice when needed, you can manage and overcome eye flu effectively.
Remember, if you suspect you have eye flu or experience persistent symptoms, consult with an eye care professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.

50 Medicines with their Uses
You are being redirected to https://www.example.com. If you are not redirected automatically, follow the link.
Some Important medicine with their uses
1. Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid)
Patient Condition: Headaches, muscle pain, fever.
2. Ibuprofen
Uses: Pain relief, anti-inflammatory.
Patient Condition: Arthritis, menstrual pain, muscle strains.
3. Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
Uses: Pain relief, fever reduction.
Patient Condition: Mild to moderate pain, fever.
4. Amoxicillin
Uses: Antibiotic, treats bacterial infections.
Patient Condition: Respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections.
5. Ciprofloxacin
Uses: Antibiotic, treats bacterial infections.
Patient Condition: Skin infections, gastrointestinal infections.
6. Fluoxetine
Uses: Antidepressant, treats depression and anxiety disorders.
Patient Condition: Major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder.
7. Lisinopril
Uses: ACE inhibitor, treats high blood pressure and heart failure.
Patient Condition: Hypertension, congestive heart failure.
8. Metformin
Uses: Antidiabetic, controls blood sugar levels.
Patient Condition: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
9. Levothyroxine
Uses: Thyroid hormone replacement.
Patient Condition: Hypothyroidism.
10. Albuterol
Uses: Bronchodilator, treats asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Patient Condition: Asthma, COPD.
11. Omeprazole
Uses: Proton pump inhibitor, reduces stomach acid production.
Patient Condition: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers.
12. Warfarin
Uses: Anticoagulant, prevents blood clot formation.
Patient Condition: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), atrial fibrillation.
13. Diazepam
Uses: Benzodiazepine, treats anxiety and muscle spasms.
Patient Condition: Anxiety disorders, muscle spasms.
14. Amlodipine
Uses: Calcium channel blocker, treats high blood pressure and angina.
Patient Condition: Hypertension, angina pectoris.
15. Simvastatin
Uses: Statin, lowers cholesterol levels.
Patient Condition: Hyperlipidemia, prevention of cardiovascular events.
16. Prednisone
Uses: Corticosteroid, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive.
Patient Condition: Inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases.
17. Cetirizine
Uses: Antihistamine, treats allergies and hives.
Patient Condition: Allergic rhinitis, urticaria.
18. Losartan
Uses: ARB (Angiotensin II receptor blocker), treats high blood pressure.
Patient Condition: Hypertension.
19. Metoprolol
Uses: Beta-blocker, treats high blood pressure and angina.
Patient Condition: Hypertension, angina pectoris.
20. Sildenafil
Uses: Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor, treats erectile dysfunction.
Patient Condition: Erectile dysfunction.
21. Amitriptyline
Uses: Tricyclic antidepressant, treats depression and certain chronic pain conditions.
Patient Condition: Major depressive disorder, neuropathic pain.
22. Aspirin + Clopidogrel
Uses: Antiplatelet agents, prevent blood clot formation.
Patient Condition: Acute coronary syndrome, secondary stroke prevention.
23. Metoprolol + Hydrochlorothiazide
Uses: Combination drug for hypertension.
Patient Condition: Hypertension.
24. Atenolol
Uses: Beta-blocker, treats high blood pressure and angina.
Patient Condition: Hypertension, angina pectoris.
25. Naproxen
Uses: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), pain relief and anti-inflammatory.
Patient Condition: Arthritis, musculoskeletal pain.
26. Metronidazole
uses: Antibiotic, treats bacterial and protozoal infections.
Patient Condition: Bacterial vaginosis, amebiasis.
27. Tamsulosin
Uses: Alpha-blocker, treats benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Patient Condition: BPH, urinary retention.
28. Ranitidine
Uses: H2 blocker, reduces stomach acid production.
Patient Condition: Peptic ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
29. Hydrochlorothiazide
Uses: Diuretic, treats edema and hypertension.
Patient Condition: Hypertension, edema.
30. Metformin + Sitagliptin
Uses: Antidiabetic combination, controls blood sugar levels.
Patient Condition: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
31. Olanzapine
Uses: Atypical antipsychotic, treats schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Patient Condition: Schizophrenia, bipolar disorder.
32. Gabapentin
Uses: Anticonvulsant, treats epilepsy and neuropathic pain.
Patient Condition: Epilepsy, neuropathic pain.
33. Furosemide
Uses: Loop diuretic, treats edema and hypertension.
Patient Condition: Edema, hypertension.
34. Clopidogrel
Uses: Antiplatelet agent, prevents blood clot formation.
Patient Condition: Acute coronary syndrome, secondary stroke prevention.
35. Montelukast
Uses: Leukotriene receptor antagonist, treats asthma and allergic rhinitis.
Patient Condition: Asthma, allergic rhinitis.
36. Venlafaxine
Uses: Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), treats depression and anxiety disorders.
Patient Condition: Major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder.
37. Pantoprazole
Uses: Proton pump inhibitor, reduces stomach acid production.
Patient Condition: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers.
38. Carvedilol
Uses: Beta-blocker, treats heart failure and hypertension.
Patient Condition: Heart failure, hypertension.
39. Lorazepam
Uses: Benzodiazepine, treats anxiety disorders and seizures.
Patient Condition: Anxiety disorders, seizures.
40. Morphine
Uses: Opioid analgesic, treats severe pain.
Patient Condition: Severe pain, post-surgery pain.
41. Cloxacillin
Uses: Antibiotic, treats bacterial infections.
Patient Condition: Skin and soft tissue infections, respiratory infections.
42. Tramadol
Uses: Opioid analgesic, treats moderate to severe pain.
Patient Condition: Moderate to severe pain.
43. Fluticasone
Uses: Corticosteroid, treats asthma and allergic rhinitis.
Patient Condition: Asthma, allergic rhinitis.
44. Rabeprazole
Uses: Proton pump inhibitor, reduces stomach acid production.
Patient Condition: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers.
45. Glimepiride
Uses: Antidiabetic, controls blood sugar levels.
Patient Condition: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
46. Doxycycline
Uses: Antibiotic, treats bacterial infections.
Patient Condition: Acne, respiratory infections.
47. Escitalopram
Uses: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), treats depression and anxiety disorders.
Patient Condition: Major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder.
48. Esomeprazole
Uses: Proton pump inhibitor, reduces stomach acid production.
Patient Condition: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers.
49. Tranexamic Acid
Uses: Hemostatic agent, controls bleeding.
Patient Condition: Excessive bleeding, menorrhagia.
50. Atorvastatin
Uses: Statin, lowers cholesterol levels.
Patient Condition: Hyperlipidemia, prevention of cardiovascular events.

.png)



.jpg)



















.jpg)




